Health Risks of Metal AM Materials
Research Studies
3D printing has existed for more than 30 years, but the rate of adoption of this technology is expanding and codes are in a race to catch up.
When determining how to evaluate a facility and whether it meets all the national and local safety codes and standards, it can be difficult to find a single go to place to find those requirements and understand how they apply. UL 3400, Outline of Investigation for Additive Manufacturing Facility Safety Management, is an evolving document that has compiled all applicable standards, best practices and guides into a single reference.
Safety Considerations for Additive Manufacturing and 3D printing
This organization, UL, offers a document outlining best practices and standards for $125-150. As they say, "this technology is expanding faster than the codes and standards for safe usage."
Study of the Environmental Implications of Using Metal Powder in Additive Manufacturing and Its Handling (Feb 2020)
Highlights:
-
The use of small powder particles, see Figure 4b, involves serious hazards to human health and the environment. Every powder container must be properly labeled, and the corresponding hazard classification must be indicated. CLP hazard pictograms are found on all powder bottles
-
The powders analyzed are composed of 45–150µm diameter particles, which is a typical value for DED applications, and therefore, the analyzed hazards are applied to that particle size. Smaller diameter particles may generate other health and environmental issues not studied in the present case
-
Titanium Ti6Al4V hazard classifications:
- H315: Causes skin irritation
- H319: Causes serious eye irritation
- H334: May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled
-
AISI 316L (Stainless Steel) hazard classifications:
- H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction
- H351: Suspected of causing cancer
- H372: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure
- H412: Harmful to aquatic life with long-lasting effects
-
Aluminum classifications:
- H261: In contact with water releases flammable gas
- H228: Flammable solid
-
Titanium classifications:
- H228: Flammable solid
- H315: Causes skin irritation
- H335: May cause respiratory irritation
-
Nickel classifications:
- H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction
- H351: Suspected of causing cancer
- H372: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure
- H412: Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects
-
In welding, airborne nanoscale metal particles are known to be hazardous to human health, and in AM processes these particles may also be generated
-
There is a need for careful design and consistent regulation of AM environments, but until this situation is reached, the implementation of preventive actions by the company can reduce the workers’ metal exposure. The most important safety measures are:
- Ventilation: The exposure can be considerably reduced by the implementation of good general ventilation which allows for the reduction of particles and fibers in the working environment. It can be further improved by point ventilation placed at strategic emission sources. Furthermore, to protect the outdoor environment, particle/fiber collection filters should be installed.
- Protective mask: Machine operators should wear a personal protective mask in the working environment where emission occurs. The mask is considered the most effective personal protective equipment
- Machine enclosure: A proper cabinet is required to prevent particles from spreading through the workshop
Exposure, assessment, and health hazards of particulate matter in metal additive manufacturing: A review (Nov 2020)
These particles can be inhaled by the respiratory system, or possibly penetrate the body through the skin and eyes. The human body cannot easily metabolize most of these powders, and their accumulation can quickly reach toxic levels. Therefore, understanding the risks of exposure to metallic particulate matter(PM) during metal 3D printing is critically important
Highlights:
- 3D printing leads to metal particulate matter pollution in environment.
- Metal particulate matter has high health impacts to humans with close contact.
- Toxicity of PM has high relations to their characteristics and exposure routes.
- High requirements for the research of exposure assessment techniques in 3D printing.
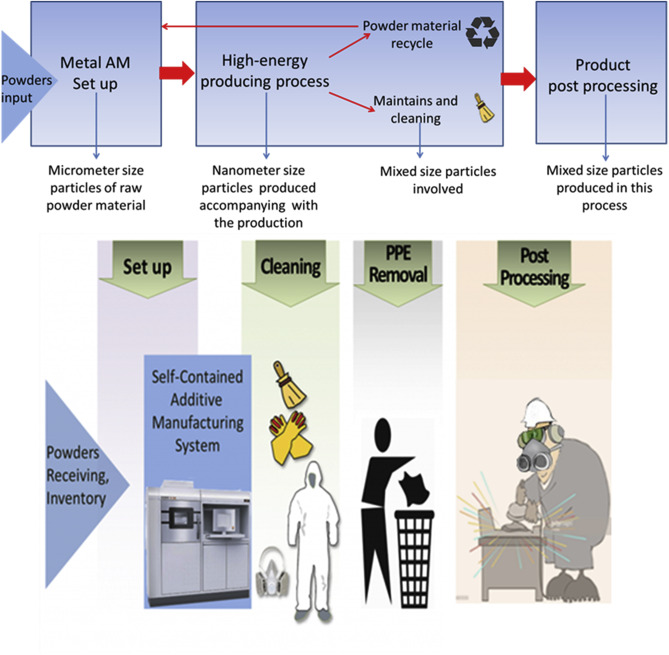
Safety in additive manufacturing: Fine dust measurements for a process chain in Laser beam melting of metals (2017)
Highlights:
- Guidelines concerning safety in additive manufacturing are not available yet (VDI , ISO, ASTM) and the topic is not completely evaluated
- Pre- and post-AM processes that cannot be automatically performed in a sealed chamber are major sources of inhalation exposure. The measured values show a broad spread of metal PM, but were not sufficient for statistical evaluation. Individual working methods, installed capture systems and the ventilation conditions in the enterprises concerned have a major effect on exposure.
Biomonitoring of Metal Exposure During Additive Manufacturing (Dec 2019)
Highlights:
- Measured airborne particle concentrations, analyzed filters used for metal content, monitored urine and dermal concentrations among AM operators, office personnel, and welders on site
- What materials were being printed? What safety precautions were taken by operators?
- Total inhalable dust levels were almost all below occupational exposure limits, however AM operators had a significant increase in cobalt exposure compared with welders