Antennas
Basics
Antennas 101(ARRL.org)
Simple Gain Antennas for the beginner (ARRL)
Ham Radio Antennas (hamradioprep.com)
Antennas Part 1: Exploring the Fundamentals of Antennas (YouTube)
Antennas Part 2: Radiation Demo & Antenna Modeling (YouTube)
Antennas Part 3: DIY HF Antenna for Ionospheric Propagation
Antennas to Buy
See Antennas for Amateur Radio
For accessories related to antennas, see Accessories for Amateur Radio
Anatomy of an Antenna
- Radiator: the portion of the antenna that RF radiation emanates from.
- Counterpoise and Radials
- Balun
- Choke
- Feed line
- Loading Coils
- Antenna tuner
- Grounding system
Sizing an antenna
Vertical size of waves:
Example:
If one is aiming for 146 MHz:
300 / 146 = ~2m
2m x 39 = ~80in
So a half-wave antenna would be ~40 in
A quarter-wave would be ~20in.
Dipole Size Calculation: 468 / f
Dipole Calculator
J-pole Calculator
1/4 Wave Ground Plane Antenna Calculator
There is an iOS app that provides these calcuations: Antenna Tool
Simulation Tools
Tuning an Antenna
A perfect SWR is 1:1 ratio. This is the ideal but not actually possible to reach this in any terrestrial setting.
Good SWR would be around 1.10:1 – 1.25:1. An OK reading would be 1.4:1.
Very good antenna analyzer may cost between $300 - $1000. Some radios have a built in SWR meter.
Many SWR meters can also be used as a wattmeter to measure the reflected power (watts) of the antenna. A well tuned antenna should maintain
Antenna Analyzers:
Types
Video about home brew antennas and terms
Dipole
Dipoles (Wikipedia) are cheap and easy to make.
Dipole Calculator
Dipole length: (468/f) / 2 = length of each side
Pros:
- simple, effective, efficient
- Easy to put up
Cons: - Likes to be higher up
- Less of a long distance antenna (DX)
Examples:
- Sotabeams Linked Dipole kit
Slim Jim
Slim jim antennas are end-fed folded dipole antennas.
- N9TAX slim jim (2m / 70cm)
Other antennas
See ARRL Antenna Book for more on antennas.
Also see ARRL Antenna Book for Radio Communications 4 volume set for 4 volumes worth on antennas.
Related concepts
Standing Wave Ratio (SWR)
An SWR meter indirectly measures the degree of mismatch between a transmission line and its load (the antenna). SWR is the ratio of reflected power back to your radio. When you key the radio, voltage is sent down the transmission line. In an RF perfect world, with a perfect antenna, a 1:1 match would mean all power is radiated from the antenna and no power is reflected. On earth in any given environment though, there is always a bit of a mismatch. The reflected power returns via the coax back to the radio and is retransmitted. In poor match situations, less power will be radiated.
Coax cable signal loss
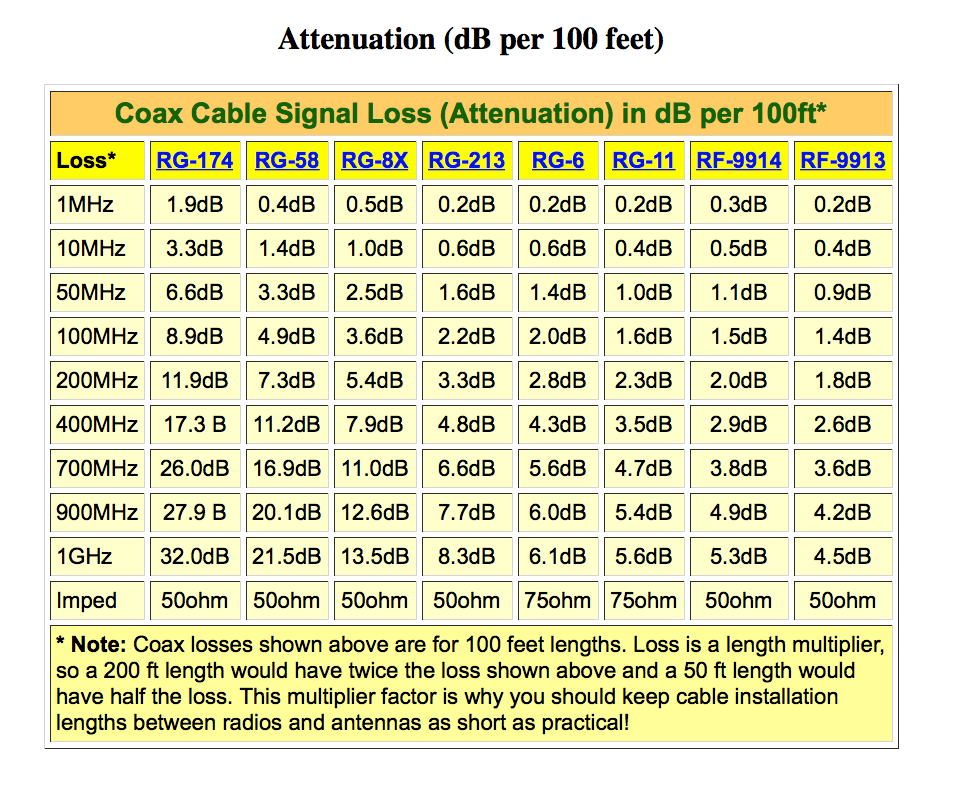
Feed line materials:
Regardless of whether you are operating at HF, VHF or UHF, the quality of your feed line is critical to your station. The feed line (also called the transmission line) is the RF power conduit between your radio and your antenna. All the energy you generate travels to the antenna through the feed line. By the same token, all the signals picked up by your antenna must reach your radio through the same feed line. For base stations in particular, always buy the lowest-loss coax you can afford.
- Ladder line: A popular type of feed line for HF use is ladder line. In fact, at HF frequencies it is the most common feed line for random-length dipoles and other antenna designs. Ladder line consists of nothing more than two wires in parallel separated by insulating material.
- RG-58 - In a mobile installation, you can use an inexpensive feed line such as RG-58 because you’re only using a short length. As long as the SWR is low, the loss will be acceptable. However, if you have an antenna that is 100 feet from your radio and you are operating at, say, 440 MHz, RG-58 would be an extraordinarily bad choice! For this installation you’ll need to invest in something much better—probably LMR-400 or Belden 9913.
- Double Shielded coax