Relays and Transistors as Switches
You can use either a transistor or a relay as the switch to control a solenoid valve with an Arduino. Each option has its advantages and specific use cases. Here's a brief overview:
Using a Transistor:
- Type: Typically, a MOSFET (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) or a BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) is used.
- Advantages:
- Size: Transistors are generally smaller than relays, making them suitable for compact designs.
- Speed: They can switch faster than relays, enabling them to be used in applications requiring high switching speeds.
- No Mechanical Parts: Being solid-state devices, they don't wear out mechanically over time.
- Considerations:
- Heat Dissipation: Power transistors may require heat sinks to manage heat, especially when driving high-current loads.
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure the transistor can handle the required load current and the voltage drop across it.
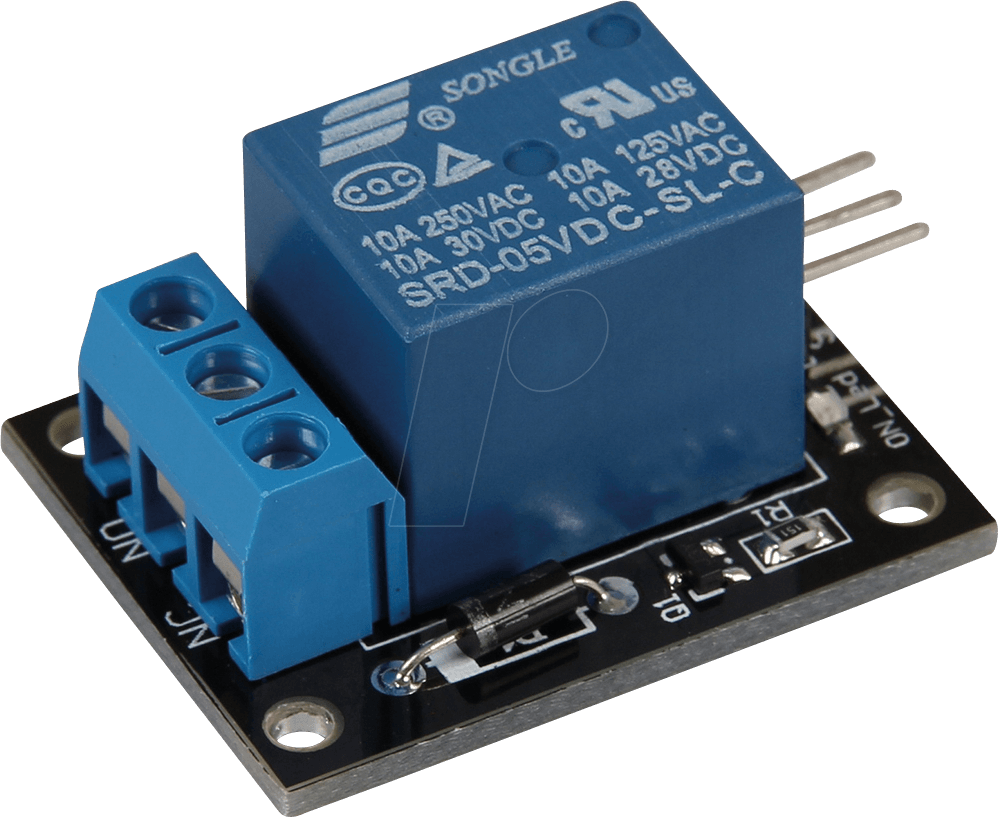
Using a Relay:
- Type: Electromechanical relays are commonly used, but solid-state relays (SSRs) are also an option.
- Advantages:
- Isolation: Relays provide excellent electrical isolation between the control circuit (Arduino) and the load (solenoid valve).
- Versatility: Suitable for switching both AC and DC loads, and can handle high voltage and current levels more easily than transistors.
- Considerations:
- Size and Noise: Relays are larger and produce an audible click sound when switching.
- Switching Speeds: Mechanical relays switch slower than transistors and have a limited lifespan due to mechanical wear and tear.
- Drive Voltage: Ensure the relay coil voltage is compatible with the Arduino's output and that the relay's contacts can handle the load current.
When choosing between a transistor and a relay, consider the following:
- The current and voltage requirements of the solenoid valve.
- The desired switching speed
- The need for electrical isolation
- Space constraints and the physical environment of the circuit (e.g., noise considerations, compactness).
For simple projects or where space and switching speed are critical, a transistor might be the better choice. For applications requiring high power handling or where electrical isolation is crucial, a relay would be preferable. Always ensure that the chosen component can handle the load requirements of your solenoid valve.